Transform retail operations with Zebra’s retail technology solutions, featuring hardware and software for improving inventory management and empowering teams.
Streamline operations with Zebra’s healthcare technology solutions, featuring hardware and software to improve staff collaboration and optimise workflows.
Enhance processes with Zebra’s manufacturing technology solutions, featuring hardware and software for automation, data analysis, and factory connectivity.
Zebra’s transportation and logistics technology solutions feature hardware and software for enhancing route planning, visibility, and automating processes.
Zebra's public sector technology solutions enhance decision-making, streamline operations, and safeguard communities with advanced software and rugged hardware.
Zebra's hospitality technology solutions equip your hotel and restaurant staff to deliver superior customer and guest service through inventory tracking and more.
Zebra's market-leading solutions and products improve customer satisfaction with a lower cost per interaction by keeping service representatives connected with colleagues, customers, management and the tools they use to satisfy customers across the supply chain.
Empower your field workers with purpose-driven mobile technology solutions to help them capture and share critical data in any environment.
Zebra's range of mobile computers equip your workforce with the devices they need from handhelds and tablets to wearables and vehicle-mounted computers.
Zebra's desktop, mobile, industrial, and portable printers for barcode labels, receipts, RFID tags and cards give you smarter ways to track and manage assets.
Zebra's 1D and 2D corded and cordless barcode scanners anticipate any scanning challenge in a variety of environments, whether retail, healthcare, T&L or manufacturing.
Zebra's extensive range of RAIN RFID readers, antennas, and printers give you consistent and accurate tracking.
Choose Zebra's reliable barcode, RFID and card supplies carefully selected to ensure high performance, print quality, durability and readability.
Zebra's rugged tablets and 2-in-1 laptops are thin and lightweight, yet rugged to work wherever you do on familiar and easy-to-use Windows or Android OS.
With Zebra's family of fixed industrial scanners and machine vision technologies, you can tailor your solutions to your environment and applications.
Zebra’s line of kiosks can meet any self-service or digital signage need, from checking prices and stock on an in-aisle store kiosk to fully-featured kiosks that can be deployed on the wall, counter, desktop or floor in a retail store, hotel, airport check-in gate, physician’s office, local government office and more.
Adapt to market shifts, enhance worker productivity and secure long-term growth with AMRs. Deploy, redeploy and optimize autonomous mobile robots with ease.
Discover Zebra’s range of accessories from chargers, communication cables to cases to help you customise your mobile device for optimal efficiency.
Zebra's environmental sensors monitor temperature-sensitive products, offering data insights on environmental conditions across industry applications.
Zebra's location technologies provide real-time tracking for your organisation to better manage and optimise your critical assets and create more efficient workflows.
Enhance frontline operations with Zebra’s AI software solutions, which optimize workflows, streamline processes, and simplify tasks for improved business outcomes.
Empower your frontline with Zebra Companion AI, offering instant, tailored insights and support to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Boost productivity with Zebra Frontline AI Enablers: AI vision models, sample apps, and APIs streamline workflows for efficient business processes.
Zebra Frontline AI Blueprints deliver adaptable, real-world AI frameworks that automate manual tasks and drive efficiency in high-pressure frontline operations.
Zebra Workcloud, enterprise software solutions boost efficiency, cut costs, improve inventory management, simplify communication and optimize resources.
Keep labour costs low, your talent happy and your organisation compliant. Create an agile operation that can navigate unexpected schedule changes and customer demand to drive sales, satisfy customers and improve your bottom line.
Drive successful enterprise collaboration with prioritized task notifications and improved communication capabilities for easier team collaboration.
Get full visibility of your inventory and automatically pinpoint leaks across all channels.
Reduce uncertainty when you anticipate market volatility. Predict, plan and stay agile to align inventory with shifting demand.
Drive down costs while driving up employee, security, and network performance with software designed to enhance Zebra's wireless infrastructure and mobile solutions.
Explore Zebra’s printer software to integrate, manage and monitor printers easily, maximising IT resources and minimising down time.
Make the most of every stage of your scanning journey from deployment to optimisation. Zebra's barcode scanner software lets you keep devices current and adapt them to your business needs for a stronger ROI across the full lifecycle.
RFID development, demonstration and production software and utilities help you build and manage your RFID deployments more efficiently.
RFID development, demonstration and production software and utilities help you build and manage your RFID deployments more efficiently.
Zebra DNA is the industry’s broadest suite of enterprise software that delivers an ideal experience for all during the entire lifetime of every Zebra device.
Advance your digital transformation and execute your strategic plans with the help of the right location and tracking technology.
Boost warehouse and manufacturing operations with Symmetry, an AMR software for fleet management of Autonomous Mobile Robots and streamlined automation workflows.
The Zebra Aurora suite of machine vision software enables users to solve their track-and-trace, vision inspection and industrial automation needs.
Zebra Aurora Focus brings a new level of simplicity to controlling enterprise-wide manufacturing and logistics automation solutions. With this powerful interface, it’s easy to set up, deploy and run Zebra’s Fixed Industrial Scanners and Machine Vision Smart Cameras, eliminating the need for different tools and reducing training and deployment time.
Aurora Imaging Library™, formerly Matrox Imaging Library, machine-vision software development kit (SDK) has a deep collection of tools for image capture, processing, analysis, annotation, display, and archiving. Code-level customisation starts here.
Aurora Design Assistant™, formerly Matrox Design Assistant, integrated development environment (IDE) is a flowchart-based platform for building machine vision applications, with templates to speed up development and bring solutions online quicker.
Designed for experienced programmers proficient in vision applications, Aurora Vision Library provides the same sophisticated functionality as our Aurora Vision Studio software but presented in programming language.
Aurora Vision Studio, an image processing software for machine & computer vision engineers, allows quick creation, integration & monitoring of powerful OEM vision applications.
Adding innovative tech is critical to your success, but it can be complex and disruptive. Professional Services help you accelerate adoption, and maximise productivity without affecting your workflows, business processes and finances.
Zebra's Managed Service delivers worry-free device management to ensure ultimate uptime for your Zebra Mobile Computers and Printers via dedicated experts.
Find ways you can contact Zebra Technologies’ Support, including Email and Chat, ask a technical question or initiate a Repair Request.
Zebra's Circular Economy Program helps you manage today’s challenges and plan for tomorrow with smart solutions that are good for your budget and the environment.
What Is Barcode Symbology?

There are many different types of barcodes, which are called Barcode Symbologies. They vary by the amount and type of encoded data (e.g., numeric only or alphanumeric). A Symbology is a defined method of representing numeric or alphabetic digits using bars and spaces that are easily scanned by computer systems. (i.e. - a specific type of barcode).
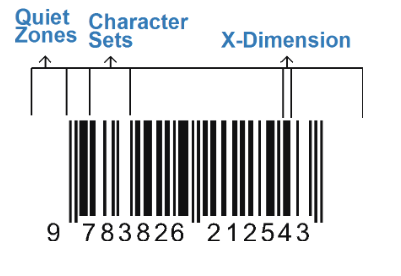
Typical characteristics of a Symbology: X-dimension: size of the smallest bar or space represented in 1/1000 of an inch (i.e. 15 mil symbol).
When you breakdown the DNA of a barcode, character sets are combinations of bars and spaces that represent a specific character. X Dimension is the width of the smallest bar or space element in the barcode which is also referred to as mil size (1 mil = .001 inch). Quiet zones are the areas just before and after the barcode.
Barcodes are divided into two main types: one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D).
How do I identify a Barcode Symbology?
Identifying a barcode symbology involves examining specific characteristics such as its structure, the type of data it encodes, and its appearance. Here’s a detailed guide to help you identify different barcode symbologies effectively:
Key Characteristics to Observe
1. Number of Dimensions:
- 1D (Linear) Barcodes: These are composed of parallel lines and spaces of varying widths.
- 2D Barcodes: These are composed of patterns like squares, dots, or other shapes that can encode more data.
2. Character Set:
- Numeric Only: Some barcodes only encode numbers.
- Alphanumeric: Others can encode both letters and numbers.
- Special Characters: Some symbologies can include special characters.
3. Structure and Appearance:
- Look at the pattern of lines, spaces, squares, or dots.
- Note the presence of start and stop characters.
- Check if there are quiet zones (blank spaces) around the barcode.
What is GS1 Barcode?
A GS1 barcode is a type of barcode that adheres to standards set by GS1, an international non-profit organization that develops and supports global standards for business communication. These barcodes are used to uniquely identify products, services, locations, and other entities in various industries, including retail, healthcare, logistics, and more. The GS1 system of standards ensures that barcodes are globally unique and universally recognizable, facilitating efficient and accurate data capture and exchange.
What Types of Barcodes Symbologies are there?
1D and 2D Symbologies do differ and therefore support different types and amounts of data. The type of barcode that is being used in the application environment will impact the type of scanner that is needed to read it.
1D Symbologies encode data horizontally along the barcode and can store a limited amount of information (around 85 characters maximum but typically much less, depending on the code type). As more data is encoded, the barcode becomes wider.
1D Barcode Symbology examples include UPC-A (Data capacity of 12 numeric digits - 11 user specified and 1 check digit), UPC-E (Data Capacity of 7 numeric digits - 6 user specified and 1 check digit), Code 128 (Variable length alphanumeric data) and I 2 of 5 (Variable length numeric data).
2D Symbologies have a two-dimensional way of representing data – both horizontally and vertically – and can store a greater amount of information (hundreds of characters), in a much smaller space, compared to a 1D code. As more data is encoded, the size of the barcode can be increased in both the horizontal and vertical directions, thus maintaining a manageable shape for easy scanning. To properly decode the data, a scanner must read the entire symbol, in both dimensions.
Examples include Data Matrix (Consists of any type of data including binary or alphanumeric and be up to 3116 bytes in length), Aztec (Consists of any type of data including binary or alphanumeric and be up to 3750 bytes in length), Maxicode (Holds up to 93 alphanumeric characters or 138 numeric digits) and QR Code (Consist of any type of data including binary or alphanumeric and be up to 7089 bytes in length).
Determining the best barcode symbology depends on the type and amount of data required, and the marking space available. The same symbology is not required for all items, because barcode scanners can recognize and decode multiple barcode formats.
Below is an overview of the main symbologies:
1D (Linear) Barcodes:
Encode data horizontally along the barcode and can store a limited amount of information (around 85 characters maximum but typically much less, depending on the code type). As more data is encoded, the barcode becomes wider. 1D Barcode Symbology examples include:

UPC & EAN (Universal Product Code / European Article Number)
Universally recognized, the UPC or EAN barcode is the most commonly used in the retail market – printed on nearly every consumer product in the world. The data is numeric only.

Code 128
Used in logistics and transportation. Often used to include information like serial numbers and expiration dates, making it a good candidate to track items through global supply chains. It supports a larger character set and can encode alphanumeric data efficiently. Can encode all 128 ASCII characters.One of the densest linear symbologies, encodes the full 128-character ASCII character set. Often used to include information like serial numbers and expiration dates, making it a good candidate to track items through global supply chains.

Code 39
Also called Code 3 of 9, it is one of the oldest and most widely used symbologies. It is a variable-length alphanumeric symbology for encoding 26 capital letters plus numerals and seven special characters. An extended version is available that supports all 128 ASCII characters. Code 39 is less dense than Code 128, thus requiring more room on the label.
Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF)
Used in warehouse and industrial applications. It is numeric-only and encodes pairs of digits
Codabar
Encodes numeric data and special characters (A, B, C, D). Used in libraries, blood banks, and photo labs. Learn more about codabar security level
MSI (Modified Plessey)
numeric-only barcode. Often used for inventory and warehouse applications.
GS1-128 (formerly known as UCC128)
A subset of Code 128 used for encoding data in a structured manner. Used in supply chains for logistics and product identification.
2D Barcodes:
It has a two-dimensional way of representing data – both horizontally and vertically – and can store a greater amount of information (hundreds of characters), in a much smaller space, compared to a 1D code. As more data is encoded, the size of the barcode can be increased in both the horizontal and vertical directions, thus maintaining a manageable shape for easy scanning. To properly decode the data, a scanner must read the entire symbol, in both dimensions. 2D Barcode Symbology examples include:

Data Matrix
A 2D symbology, Data Matrix is commonly used to mark small items as it can encode a significant amount of information in small space and is often used in pharmaceutical applications, or other operations where tracking and tracing is critical.

Aztec Code
A 2D matrix symbology containing from 13 to 3,832 numeric characters or 12 to 3,067 alphabetic characters. Aztec Mesas are Aztec Code-based supplements that enable linear barcode symbols to encode additional information. The resulting symbol is a composite of linear and 2D symbologies. Often used in transportation, especially for boarding passes and tickets. Reads well even when printed with low quality.

QR Code
This stands for Quick Response Code and is a 2D code containing 4000 – 7000 Characters. These are commonly used for mobile barcoding applications, such as loyalty cards or coupon codes.

PDF417
PDF417 is a stacked linear or two-dimensional barcode. It is commonly recognized as the barcode on many U.S. Driver’s Licenses, but can also be used for other applications related to transportation or inventory management. Data is encoded in both the horizontal and vertical dimensions. As more data is encoded, the size of the barcode can be increased in both the horizontal and vertical directions thus maintaining a manageable shape for easy scanning.
MaxiCode
Used by United Parcel Service (UPS) for package tracking. Designed for fast and accurate reading in shipping environments.
Specialized and Proprietary Barcodes:
Pharmacode
Used in the pharmaceutical industry for tracking and identifying medications. Can encode numeric data and is designed for high-reliability scanning. Learn more about pharmacode by visiting this FAQ: What is a Pharmacode?
Where Are Different Symbologies Used?
Each barcode symbology has unique features that make it suitable for specific applications and industries. Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right barcode for their needs, enhancing operational efficiency, accuracy, and traceability. By selecting the appropriate barcode symbology, organizations can streamline their processes, improve data management, and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
| 1D (Linear) Barcodes: | Popular Applications |
| UPC: EAN-13: Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF): Codabar: | Most Retail Products in US - High Volume Scanning International Retail Products Shipping, Laboratories, Warehouse, Industrial Apps Libraries, Blood Banks, Overnight Package Delivery |
| 1D Alpha-Numeric Codes: | |
| Code 128: Code 39: | Shipping |
| 2D Barcodes: | |
PDF417: Aztec Code: | File Driver’s Licenses and other Identification cards, boarding passes, inventory Transportation, particularly for boarding passes and tickets. |
| Especialized and Proprietary Barcodes | |
| Pharmacode: | Pharmaceutical industry, Medication tracking and identification Libraries and asset tracking, book tracking, asset management, inventory control |
Explore Our Barcode Scanner And Data Capture Products
Legal Terms of Use Privacy Policy Supply Chain Transparency
ZEBRA and the stylized Zebra head are trademarks of Zebra Technologies Corp., registered in many jurisdictions worldwide. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Note: Some content or images on zebra.com may have been generated in whole or in part by AI. ©2026 Zebra Technologies Corp. and/or its affiliates.