Transform retail operations with Zebra’s retail technology solutions, featuring hardware and software for improving inventory management and empowering teams.
Streamline operations with Zebra’s healthcare technology solutions, featuring hardware and software to improve staff collaboration and optimise workflows.
Enhance processes with Zebra’s manufacturing technology solutions, featuring hardware and software for automation, data analysis, and factory connectivity.
Zebra’s transportation and logistics technology solutions feature hardware and software for enhancing route planning, visibility, and automating processes.
Zebra's hospitality technology solutions equip your hotel and restaurant staff to deliver superior customer and guest service through inventory tracking and more.
Zebra's market-leading solutions and products improve customer satisfaction with a lower cost per interaction by keeping service representatives connected with colleagues, customers, management and the tools they use to satisfy customers across the supply chain.
Empower your field workers with purpose-driven mobile technology solutions to help them capture and share critical data in any environment.
Zebra's range of mobile computers equip your workforce with the devices they need from handhelds and tablets to wearables and vehicle-mounted computers.
Zebra's desktop, mobile, industrial, and portable printers for barcode labels, receipts, RFID tags and cards give you smarter ways to track and manage assets.
Zebra's 1D and 2D corded and cordless barcode scanners anticipate any scanning challenge in a variety of environments, whether retail, healthcare, T&L or manufacturing.
Zebra's extensive range of RAIN RFID readers, antennas, and printers give you consistent and accurate tracking.
Choose Zebra's reliable barcode, RFID and card supplies carefully selected to ensure high performance, print quality, durability and readability.
Zebra's rugged tablets and 2-in-1 laptops are thin and lightweight, yet rugged to work wherever you do on familiar and easy-to-use Windows or Android OS.
With Zebra's family of fixed industrial scanners and machine vision technologies, you can tailor your solutions to your environment and applications.
Zebra’s line of kiosks can meet any self-service or digital signage need, from checking prices and stock on an in-aisle store kiosk to fully-featured kiosks that can be deployed on the wall, counter, desktop or floor in a retail store, hotel, airport check-in gate, physician’s office, local government office and more.
Discover Zebra’s range of accessories from chargers, communication cables to cases to help you customise your mobile device for optimal efficiency.
Zebra's environmental sensors monitor temperature-sensitive products, offering data insights on environmental conditions across industry applications.
Zebra's location technologies provide real-time tracking for your organisation to better manage and optimise your critical assets and create more efficient workflows.
Enhance frontline operations with Zebra’s AI software solutions, which optimize workflows, streamline processes, and simplify tasks for improved business outcomes.
Empower your frontline with Zebra Companion AI, offering instant, tailored insights and support to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
The everything you need to rapidly and cost effectively develop high-performance AI vision applications on Zebra mobile computers.
Zebra Workcloud, enterprise software solutions boost efficiency, cut costs, improve inventory management, simplify communication and optimize resources.
Keep labour costs low, your talent happy and your organisation compliant. Create an agile operation that can navigate unexpected schedule changes and customer demand to drive sales, satisfy customers and improve your bottom line.
Drive successful enterprise collaboration with prioritized task notifications and improved communication capabilities for easier team collaboration.
Get full visibility of your inventory and automatically pinpoint leaks across all channels.
Reduce uncertainty when you anticipate market volatility. Predict, plan and stay agile to align inventory with shifting demand.
Drive down costs while driving up employee, security, and network performance with software designed to enhance Zebra's wireless infrastructure and mobile solutions.
Explore Zebra’s printer software to integrate, manage and monitor printers easily, maximising IT resources and minimising down time.
Make the most of every stage of your scanning journey from deployment to optimisation. Zebra's barcode scanner software lets you keep devices current and adapt them to your business needs for a stronger ROI across the full lifecycle.
RFID development, demonstration and production software and utilities help you build and manage your RFID deployments more efficiently.
RFID development, demonstration and production software and utilities help you build and manage your RFID deployments more efficiently.
Zebra DNA is the industry’s broadest suite of enterprise software that delivers an ideal experience for all during the entire lifetime of every Zebra device.
Advance your digital transformation and execute your strategic plans with the help of the right location and tracking technology.
The Zebra Aurora suite of machine vision software enables users to solve their track-and-trace, vision inspection and industrial automation needs.
Zebra Aurora Focus brings a new level of simplicity to controlling enterprise-wide manufacturing and logistics automation solutions. With this powerful interface, it’s easy to set up, deploy and run Zebra’s Fixed Industrial Scanners and Machine Vision Smart Cameras, eliminating the need for different tools and reducing training and deployment time.
Aurora Imaging Library™, formerly Matrox Imaging Library, machine-vision software development kit (SDK) has a deep collection of tools for image capture, processing, analysis, annotation, display, and archiving. Code-level customisation starts here.
Aurora Design Assistant™, formerly Matrox Design Assistant, integrated development environment (IDE) is a flowchart-based platform for building machine vision applications, with templates to speed up development and bring solutions online quicker.
Designed for experienced programmers proficient in vision applications, Aurora Vision Library provides the same sophisticated functionality as our Aurora Vision Studio software but presented in programming language.
Aurora Vision Studio, an image processing software for machine & computer vision engineers, allows quick creation, integration & monitoring of powerful OEM vision applications.
Adding innovative tech is critical to your success, but it can be complex and disruptive. Professional Services help you accelerate adoption, and maximise productivity without affecting your workflows, business processes and finances.
Zebra's Managed Service delivers worry-free device management to ensure ultimate uptime for your Zebra Mobile Computers and Printers via dedicated experts.
Find ways you can contact Zebra Technologies’ Support, including Email and Chat, ask a technical question or initiate a Repair Request.
Zebra's Circular Economy Program helps you manage today’s challenges and plan for tomorrow with smart solutions that are good for your budget and the environment.
What Is RTLS?

What Is RTLS (Real-Time Location Systems)?
RTLS stands for Real-time Location System and encompasses several automated identification (auto-ID) technologies that use wireless signals to determine the precise location of tagged assets or personnel. At its core, RTLS employs a combination of hardware, software and communication technologies to determine and relay the real-time location of tagged items or people within a defined area of interest. It is crucial to understand that RTLS is not a singular type of system or technology, but rather a desired outcome that can be achieved through diverse systems employed for asset tracking and management. A fundamental aspect of RTLS revolves around the time dimension in which different assets are monitored and the resulting data can be leveraged in various ways depending on the specific application requirements.
RTLS systems include “active” transponder tags that transmit a long-range signal (up to thousands of meters with ISO / IEC 24730-2) at regular intervals, location sensors that receive and process tag signals, and a location appliance that collects and correlates the data. In contrast, “passive” radio frequency identification (RFID) systems have a very short range (up to twenty meters) and only read the tags when a reader is near.
Passive tagging only presents visibility for a small segment of time when the asset passes within range of a reader. As a result, tracking systems may miss a critical time window to capture location information essential for applications with a constantly changing state. Passive technologies like RFID and barcodes are optimal solutions for a wide range of structured traceability applications where range and short time windows are not critical.
How Does RTLS Work?
Anything being tracked by an RTLS has a tag affixed to it which can be located by the infrastructure of the system. An alternate implementation can leverage devices that are location aware (i.e. can determine their own location) and can report their location to the infrastructure (e.g. cell phone for GPS tracking).
The foundation of an RTLS solution lies in the deployment of tags or badges that are attached to the objects to be tracked. These tags utilize various technologies such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), infrared, ultrasound or Wi-Fi to transmit signals containing unique identifiers and location data. The transmitted signals are then received and processed by a network of sensors, receivers or reference points strategically placed throughout the environment. The tag or location-aware device stores the unique identity and sometimes additional information (e.g. current and fast location, users of the object, product origin, physical conditions, maintenance records, compliance, etc.) about the object on which it is attached or representing.
The information stored on these devices along with the real-time positioning of the object is then communicated back to an associated business system. A typical topology provides real-time visibility, normally via a map or (graphical user interface), as well as associated real-time planning, execution and reporting functions.
The data may also be integrated into a wider ERP (Enterprise resource planning) solution by providing updates to key business processes such as warehouse management, production planning/scheduling, transportation planning and other related applications.
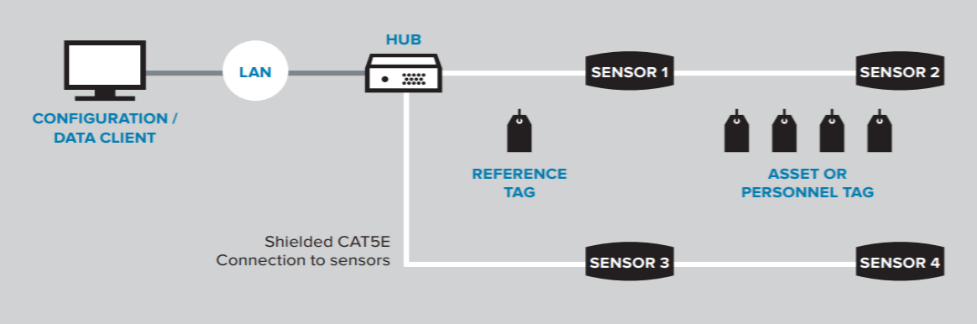
An active solution is made up of three primary layers, The first is the physical layer which comprises the tags and the receivers. These tangible components feed data into the next, or base business process layer. This is a software application within the broad ERP system that will do one or multiple functions such as providing location information on assets, or possibly managing material flows within a production environment.
The third and final layer is the business process analysis. This stems from the intelligence that is gathered from the previous business process layer. Essentially organizations are discovering that by using the data that is extracted from the location solutions platform they are able to make more informed decisions and take actions enabling them to better optimize their business.
What Is an RTLS Sensor?
RTLS Sensors, such as data loggers, play a vital role in monitoring the physical environment surrounding an object or asset. These sensors are employed to capture and track various environmental parameters that provide valuable insights into the conditions experienced by the object throughout its journey or storage.
One of the primary functions of RTLS Sensors is to receive and process tag signals. These signals are transmitted by the tags attached to the objects being monitored. By capturing these signals, the sensors can accurately determine the location of the objects within the defined RTLS infrastructure.
In addition to location tracking, RTLS Sensors commonly incorporate various environmental sensors to gather data related to temperature and humidity. These sensors enable real-time monitoring and recording of the ambient conditions in which the object is situated. Temperature sensors provide information about the thermal profile, ensuring that temperature-sensitive items are stored within specified ranges. Humidity sensors, on the other hand, measure the moisture content in the surrounding environment, which is crucial for sensitive materials or products that may be susceptible to damage or degradation in high humidity conditions.
By integrating temperature and humidity sensors into the RTLS system, organizations can ensure the optimal conditions for the objects being tracked. This data enables proactive management, early identification of potential issues, and the ability to take timely corrective actions if deviations from desired environmental conditions occur.
What Is the Difference Between RTLS and GPS?
While Global Positioning Systems (GPS) offer some RTLS capabilities, GPS signals cannot penetrate most construction materials, leaving indoor facilities inaccessible. Furthermore, GPS receivers are highly complex, costly, and require significantly more power than RTLS tags, and lack fine-grained accuracy. Ultra-wideband (UWB) RTLS tags have an accuracy greater than one foot and consume minimal power.
Unlike traditional GPS systems that offer global coverage, RTLS focuses on localized tracking in indoor or confined environments such as buildings, warehouses, or healthcare facilities. Real-Time Location Systems find extensive application in indoor and confined environments where they offer precise tracking and management capabilities. In short, RTLS does not provide global coverage like a Global Positioning System. Instead, RTLS focuses on localized tracking within designated areas.
To facilitate tracking and management, RTLS tags are securely attached to mobile items that require monitoring. These tags transmit signals containing valuable location information, allowing organizations to track and manage the movement and whereabouts of these items in real-time.
Depending on the RTLS application, tags contain a battery life of up to seven years. RTLS tags can attach to forklifts, containers, hospital and test equipment, trailers and containers, and personnel identification cards. RTLS tags feature programable transmit rates and support a configurable “blink” rate that sends out identification and telemetry data at fixed intervals.
Once activated, the tag transmits a signal to identify its precise location. Location sensors allow flexible placement in and around a facility, a shipping yard, on light poles, or on corners of outdoor buildings. The combination of location data from the RTLS system and the telemetry data enables a nearly unlimited set of applications.
Within the RTLS infrastructure, reference points play a critical role. These reference points can take the form of transmitters or receivers and are strategically placed throughout the building or the specific area of interest. The purpose of these reference points is to ensure comprehensive coverage of the tags within the designated area. By strategically deploying reference points, organizations can achieve greater location accuracy for the tracked items.
It is worth noting that the installation of more RTLS reference points generally improves location accuracy, up to the limitations of the technology itself. Therefore, careful planning and consideration are necessary to strike the right balance between the number of reference points deployed and the desired level of accuracy.
There are many different location technologies available in today's market that empower businesses to use RTLS based on their needs. RTLS encompasses various system designs, all falling under the umbrella of real-time locating systems. Two primary system design elements commonly employed are locating at choke points and locating in relative coordinates. Locating at choke points refers to the placement of reference points at specific areas where items must pass through, such as entrances, exits, corridors or checkpoints. By focusing on these choke points, organizations can track the movement and flow of items through critical areas, ensuring efficient operations and enhanced security. On the other hand, locating in relative coordinates involves establishing a coordinate system within the designated area of interest. The reference points serve as anchor points for defining these relative coordinates, enabling precise tracking and localization of the tagged items within the established coordinate system. This method allows organizations to understand the exact position and relative distances between different items, facilitating efficient asset management and optimization of workflows.
What Are the Benefits of RTLs?
Using RTLS technology gives specialized teams complete visibility of the physical location and current status of equipment. One of the key advantages of RTLS is its ability to provide real-time location information, allowing organizations to monitor the movement and status of assets or people instantaneously. This up-to-the-minute data empowers decision-makers to respond promptly, enhance operational workflows, and improve overall situational awareness.
RTLS eliminates the need to spend considerable manpower searching for equipment. Instead, the technology enables teams to move ahead with usage or maintenance and make informed decisions. By automating the tracking of the flight line equipment, you reduce the manpower required to maintain and update status, lower equipment costs and improve mission effectiveness.
RTLS immediately enhances all aspects of your operations from improving team efficiency to shortening maintenance downtime to preventing property loss. Zebra Technologies' solution allows you to always know the location and status of flight line equipment without the typical manual searching. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) all but eliminates the need for onsite and manual checking. Instead, you can view the location and status of an asset on screen.
With RTLS, you keep team members on valuable tasks, allowing them to focus on core activities thus increasing your operational efficiency. Additionally, teams can respond more rapidly to user requests, expedite maintenance and reduce missing items. Furthermore, RTLS systems can be designed to address diverse use cases and industry-specific requirements. For instance, in manufacturing settings, RTLS helps track and optimize the flow of materials, monitor inventory levels, and streamline production processes. In healthcare facilities, RTLS enables efficient asset management, enhances patient safety through staff and equipment tracking and aids in workflow optimization.
Real-Time Locating Systems offer organizations a powerful means of tracking and managing assets and equipment in real-time. A truly optimal Real Time Location System excels in accurately locating, tracking and managing a wide array of assets and inventory. By harnessing the wealth of location data collected, organizations are empowered to make well-informed decisions that drive operational efficiency and effectiveness. When businesses leverage advanced technologies and deploy tags, sensors and reference points, they can use RTLS to enable improved operational productivity, enhanced safety measures and better resource utilization. With its wide range of applications across industries, RTLS continues to revolutionize how businesses track, manage, and optimize their valuable assets in today's dynamic and fast-paced world.
Explore Our Range of Location Technologies
Legal Terms of Use Privacy Policy Supply Chain Transparency
ZEBRA and the stylized Zebra head are trademarks of Zebra Technologies Corp., registered in many jurisdictions worldwide. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Note: Some content or images on zebra.com may have been generated in whole or in part by AI. ©2025 Zebra Technologies Corp. and/or its affiliates.