Transform retail operations with Zebra’s retail technology solutions, featuring hardware and software for improving inventory management and empowering teams.
Streamline operations with Zebra’s healthcare technology solutions, featuring hardware and software to improve staff collaboration and optimise workflows.
Enhance processes with Zebra’s manufacturing technology solutions, featuring hardware and software for automation, data analysis, and factory connectivity.
Zebra’s transportation and logistics technology solutions feature hardware and software for enhancing route planning, visibility, and automating processes.
Zebra's hospitality technology solutions equip your hotel and restaurant staff to deliver superior customer and guest service through inventory tracking and more.
Zebra's market-leading solutions and products improve customer satisfaction with a lower cost per interaction by keeping service representatives connected with colleagues, customers, management and the tools they use to satisfy customers across the supply chain.
Empower your field workers with purpose-driven mobile technology solutions to help them capture and share critical data in any environment.
Zebra's range of mobile computers equip your workforce with the devices they need from handhelds and tablets to wearables and vehicle-mounted computers.
Zebra's desktop, mobile, industrial, and portable printers for barcode labels, receipts, RFID tags and cards give you smarter ways to track and manage assets.
Zebra's 1D and 2D corded and cordless barcode scanners anticipate any scanning challenge in a variety of environments, whether retail, healthcare, T&L or manufacturing.
Zebra's extensive range of RAIN RFID readers, antennas, and printers give you consistent and accurate tracking.
Choose Zebra's reliable barcode, RFID and card supplies carefully selected to ensure high performance, print quality, durability and readability.
Zebra's rugged tablets and 2-in-1 laptops are thin and lightweight, yet rugged to work wherever you do on familiar and easy-to-use Windows or Android OS.
With Zebra's family of fixed industrial scanners and machine vision technologies, you can tailor your solutions to your environment and applications.
Zebra’s line of kiosks can meet any self-service or digital signage need, from checking prices and stock on an in-aisle store kiosk to fully-featured kiosks that can be deployed on the wall, counter, desktop or floor in a retail store, hotel, airport check-in gate, physician’s office, local government office and more.
Discover Zebra’s range of accessories from chargers, communication cables to cases to help you customise your mobile device for optimal efficiency.
Zebra's environmental sensors monitor temperature-sensitive products, offering data insights on environmental conditions across industry applications.
Zebra's location technologies provide real-time tracking for your organisation to better manage and optimise your critical assets and create more efficient workflows.
Enhance frontline operations with Zebra’s AI software solutions, which optimize workflows, streamline processes, and simplify tasks for improved business outcomes.
Empower your frontline with Zebra Companion AI, offering instant, tailored insights and support to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Boost productivity with Zebra Frontline AI Enablers: AI vision models, sample apps, and APIs streamline workflows for efficient business processes.
Zebra Frontline AI Blueprints deliver adaptable, real-world AI frameworks that automate manual tasks and drive efficiency in high-pressure frontline operations.
Zebra Workcloud, enterprise software solutions boost efficiency, cut costs, improve inventory management, simplify communication and optimize resources.
Keep labour costs low, your talent happy and your organisation compliant. Create an agile operation that can navigate unexpected schedule changes and customer demand to drive sales, satisfy customers and improve your bottom line.
Drive successful enterprise collaboration with prioritized task notifications and improved communication capabilities for easier team collaboration.
Get full visibility of your inventory and automatically pinpoint leaks across all channels.
Reduce uncertainty when you anticipate market volatility. Predict, plan and stay agile to align inventory with shifting demand.
Drive down costs while driving up employee, security, and network performance with software designed to enhance Zebra's wireless infrastructure and mobile solutions.
Explore Zebra’s printer software to integrate, manage and monitor printers easily, maximising IT resources and minimising down time.
Make the most of every stage of your scanning journey from deployment to optimisation. Zebra's barcode scanner software lets you keep devices current and adapt them to your business needs for a stronger ROI across the full lifecycle.
RFID development, demonstration and production software and utilities help you build and manage your RFID deployments more efficiently.
RFID development, demonstration and production software and utilities help you build and manage your RFID deployments more efficiently.
Zebra DNA is the industry’s broadest suite of enterprise software that delivers an ideal experience for all during the entire lifetime of every Zebra device.
Advance your digital transformation and execute your strategic plans with the help of the right location and tracking technology.
The Zebra Aurora suite of machine vision software enables users to solve their track-and-trace, vision inspection and industrial automation needs.
Zebra Aurora Focus brings a new level of simplicity to controlling enterprise-wide manufacturing and logistics automation solutions. With this powerful interface, it’s easy to set up, deploy and run Zebra’s Fixed Industrial Scanners and Machine Vision Smart Cameras, eliminating the need for different tools and reducing training and deployment time.
Aurora Imaging Library™, formerly Matrox Imaging Library, machine-vision software development kit (SDK) has a deep collection of tools for image capture, processing, analysis, annotation, display, and archiving. Code-level customisation starts here.
Aurora Design Assistant™, formerly Matrox Design Assistant, integrated development environment (IDE) is a flowchart-based platform for building machine vision applications, with templates to speed up development and bring solutions online quicker.
Designed for experienced programmers proficient in vision applications, Aurora Vision Library provides the same sophisticated functionality as our Aurora Vision Studio software but presented in programming language.
Aurora Vision Studio, an image processing software for machine & computer vision engineers, allows quick creation, integration & monitoring of powerful OEM vision applications.
Adding innovative tech is critical to your success, but it can be complex and disruptive. Professional Services help you accelerate adoption, and maximise productivity without affecting your workflows, business processes and finances.
Zebra's Managed Service delivers worry-free device management to ensure ultimate uptime for your Zebra Mobile Computers and Printers via dedicated experts.
Find ways you can contact Zebra Technologies’ Support, including Email and Chat, ask a technical question or initiate a Repair Request.
Zebra's Circular Economy Program helps you manage today’s challenges and plan for tomorrow with smart solutions that are good for your budget and the environment.
What Is an Electronic Health Record (EHR)?
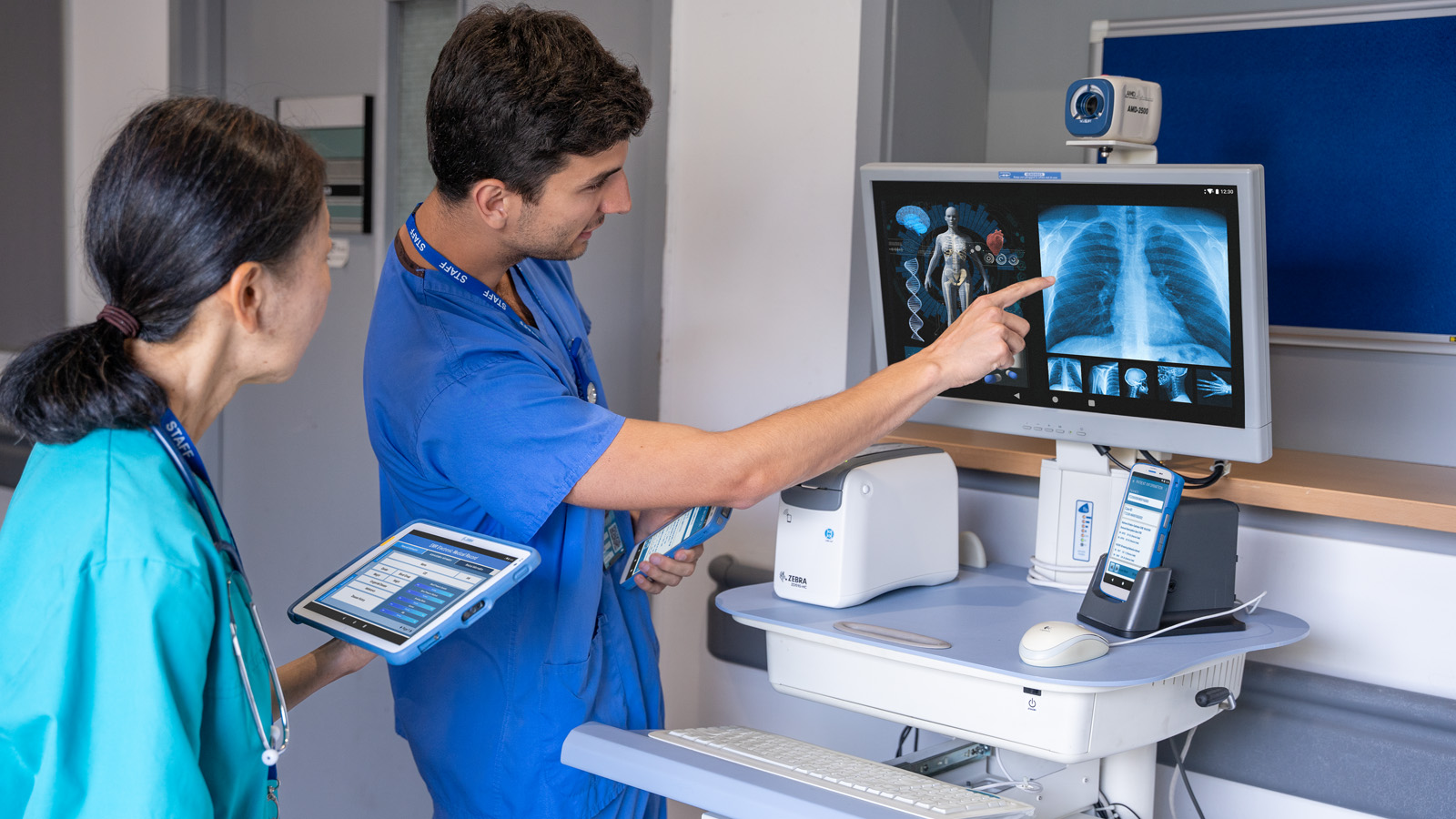
An Electronic Health Record (EHR) system is a digital version of a patient’s paper chart, providing real-time, patient-centered records that make information available instantly and securely to authorized users. EHR systems in healthcare are designed to go beyond standard clinical data collected in a provider’s office and are inclusive of a broader view of a patient’s care. They can manage a wide array of data, including demographics, medical history, medications, allergies, immunization status, laboratory test results, radiology images, and billing information. EHR systems streamline the workflow by allowing healthcare providers to access the necessary information quickly, leading to improved patient care and operational efficiencies.
How does an Electronic Health Record (EHR) system work in healthcare?
The integration of EHR systems in healthcare eases better communication among healthcare providers, thus enhancing collaborative care. In the realm of EHR healthcare, these systems centralize patient information, reducing the risk of errors, such as prescription mistakes, and improving the overall quality of healthcare delivery. This system also supports the use of evidence-based tools that can aid in decision-making and enable healthcare providers to deliver personalized patient care. Moreover, EHR systems are pivotal in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, including HIPAA, by maintaining the security and privacy of patient data.
Incorporating EHR systems in healthcare not only improves the workflow efficiency but also contributes to the strategic goals of healthcare organizations, such as cost reduction and improved patient outcomes. The ability to analyze EHR data helps healthcare providers identify trends and patterns that can inform public health strategies and interventions. The shift from paper-based records to digital systems represents a significant advancement in healthcare, offering a framework for continuous improvement and innovation in patient care delivery.
What technology is involved in implementing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems in healthcare?
Implementing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems in healthcare requires a strategic integration of both software and hardware components. This clinical solution facilitates efficient data management and enhances patient care delivery across various healthcare settings.
1. Software Components:
A key component of EHR systems is the software application, which serves as a centralized digital repository for patient information. These applications are crucial for managing and storing patient data, facilitating effective care coordination and informed clinical decision-making. By providing healthcare professionals with access to comprehensive, real-time data, software applications enhance patient outcomes and streamline healthcare operations, particularly in hospitals where managing complex care processes is essential.
2. Hardware Components:
The hardware aspect of EHR systems includes essential devices such as printers, tablets, barcode scanners, and mobile computing tools. These devices are integral to accurately capturing and accessing health data. For instance, barcode scanners and mobile computing devices enable healthcare providers to scan patient wristbands for quick retrieval of EHRs, ensuring precise medication administration and efficient documentation. This technology allows healthcare providers to seamlessly update patient records and access critical information at the point of care.
Together, these software and hardware components create a robust framework for EHR systems, ensuring efficient data management and enhancing the quality of patient care. The integration of these technologies supports healthcare providers in delivering prompt, accurate, and safe care, while also contributing to the strategic goals of healthcare organizations, such as cost reduction, improved patient outcomes, and compliance with regulatory standards.
What challenges do healthcare providers face when implementing EHR systems?
Implementing 3D imaging technologies involves various challenges, each requiring specific solutions to ensure accurate and reliable performance. Here are some common challenges associated with 3D imaging technologies and ways to mitigate them:
- Cost of Implementation:
Investing in electronic health record (EHR) systems represents a significant opportunity to improve the efficiency and quality of healthcare. It is vital that healthcare organizations invest not only in the technology itself, but also in comprehensive staff training to ensure effective use of the new systems. While these investments may require careful financial planning, they pave the way for greater operational streamlining, better resource management, and more effective patient care.
- Resistance to Change:
Transitioning to EHR systems requires significant adjustments in workflow and procedures, leading to potential resistance among healthcare providers and staff. Concerns about usability and the potential for increased workload during the transition period can hinder adoption. To overcome this resistance, it is crucial to ensure that all users receive adequate training and support, enabling them to become comfortable and proficient with the new systems.
- Data Security:
Protecting patient data from unauthorized access and breaches is a critical concern when implementing EHR systems. Healthcare providers must establish robust security measures and protocols to safeguard sensitive information. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, which mandate specific standards for data protection and privacy, is essential. Addressing these security challenges requires a proactive approach to planning and continuous monitoring to maintain high standards of data protection.
What are the benefits of using EHR software in healthcare?
Electronic Health Record (EHR) software offers numerous advantages to both healthcare providers and patients, enhancing the quality and efficiency of healthcare services. By digitizing patient records, EHRs ensure that critical information is readily accessible, accurate, and secure, promoting better healthcare outcomes and operational productivity. This digital transformation is pivotal in an era where prompt access to patient data can significantly affect the quality of care delivered. Furthermore, EHR systems are designed to support a wide array of healthcare processes, from clinical decision-making to administrative functions, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient interaction and less on paperwork. The integration of EHRs also facilitates data-driven decision-making, enabling healthcare organizations to harness insights from patient data to improve treatment protocols and patient safety measures. In addition, EHRs support compliance with regulatory requirements, such as those outlined by HIPAA, ensuring that patient privacy and data security are supported at the highest standards.
Here are some key benefits of EHR:
- Improved Patient Care and Safety: EHR software provides healthcare providers with complete and correct patient information, which helps in making informed decisions about patient care. Features such as alerts for potential drug interactions and reminders for preventive care contribute to enhanced patient safety.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: By digitizing patient records, EHR systems streamline administrative tasks such as scheduling, billing, and coding. This automation helps reduce paperwork and allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient care, thus increasing productivity.
- Enhanced Care Coordination: EHRs facilitate seamless communication among healthcare providers, ensuring that all caregivers involved in a patient’s treatment have access to the same up-to-date information. This is particularly beneficial in complex cases where multiple specialists are involved.
- Respond to Patients Faster:Technologies like Zebra’s Workcloud Sync enhance EHR systems by incorporating location tracking to monitor real-time positions of nursing staff. This capability allows healthcare facilities to show and deploy the nearest available staff members to respond swiftly to patient care needs. As a real-time communication and collaboration application, Sync also allows clinical staff to follow up efficiently with colleagues using features like push-to-talk (PTT), voice/video calling, and multimedia chat—based on their location—helping to streamline coordination and accelerate care delivery.
- Streamlined Emergency Communication: EHR systems integrated with features such as the emergency duress button improve safety by enabling quick communication with relevant safety staff during emergencies. This ensures that unsafe situations are managed promptly and effectively.
- Flexibility in Healthcare Teams: EHR systems can empower a more agile workforce by allowing healthcare professionals to switch between multiple pre-defined profiles. This flexibility enhances team communication and collaboration, enabling staff to adapt quickly to changing needs and fill gaps in coverage.
- Patient Engagement and Access: EHR systems often include patient portals that allow patients to access their health records, schedule appointments, and communicate with their healthcare providers. This empowers patients to take an active role in their healthcare management.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: EHR systems enable healthcare providers to analyze large datasets, identify trends, and generate reports that can inform clinical decisions, public health initiatives, and research efforts. Overall, EHR software significantly contributes to a more efficient, coordinated, and patient-centered healthcare system, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
Experience the future of healthcare with EHR Solutions
Legal Terms of Use Privacy Policy Supply Chain Transparency
ZEBRA and the stylized Zebra head are trademarks of Zebra Technologies Corp., registered in many jurisdictions worldwide. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Note: Some content or images on zebra.com may have been generated in whole or in part by AI. ©2026 Zebra Technologies Corp. and/or its affiliates.