Automate weld verification on frames and panels with smart cameras, 3D profiling, and software that manage glare and dense weld patterns
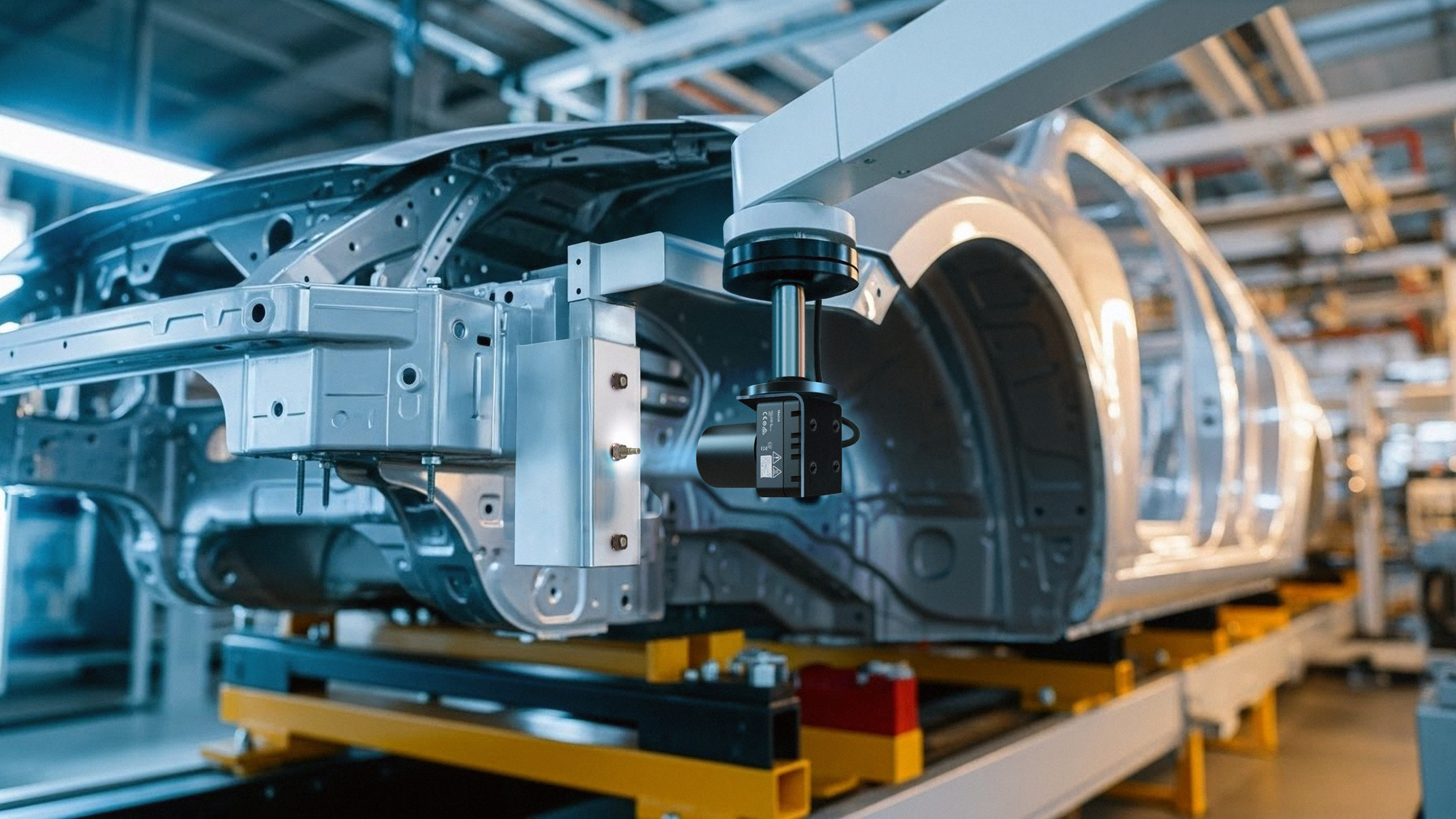

Detect welding defects effectively
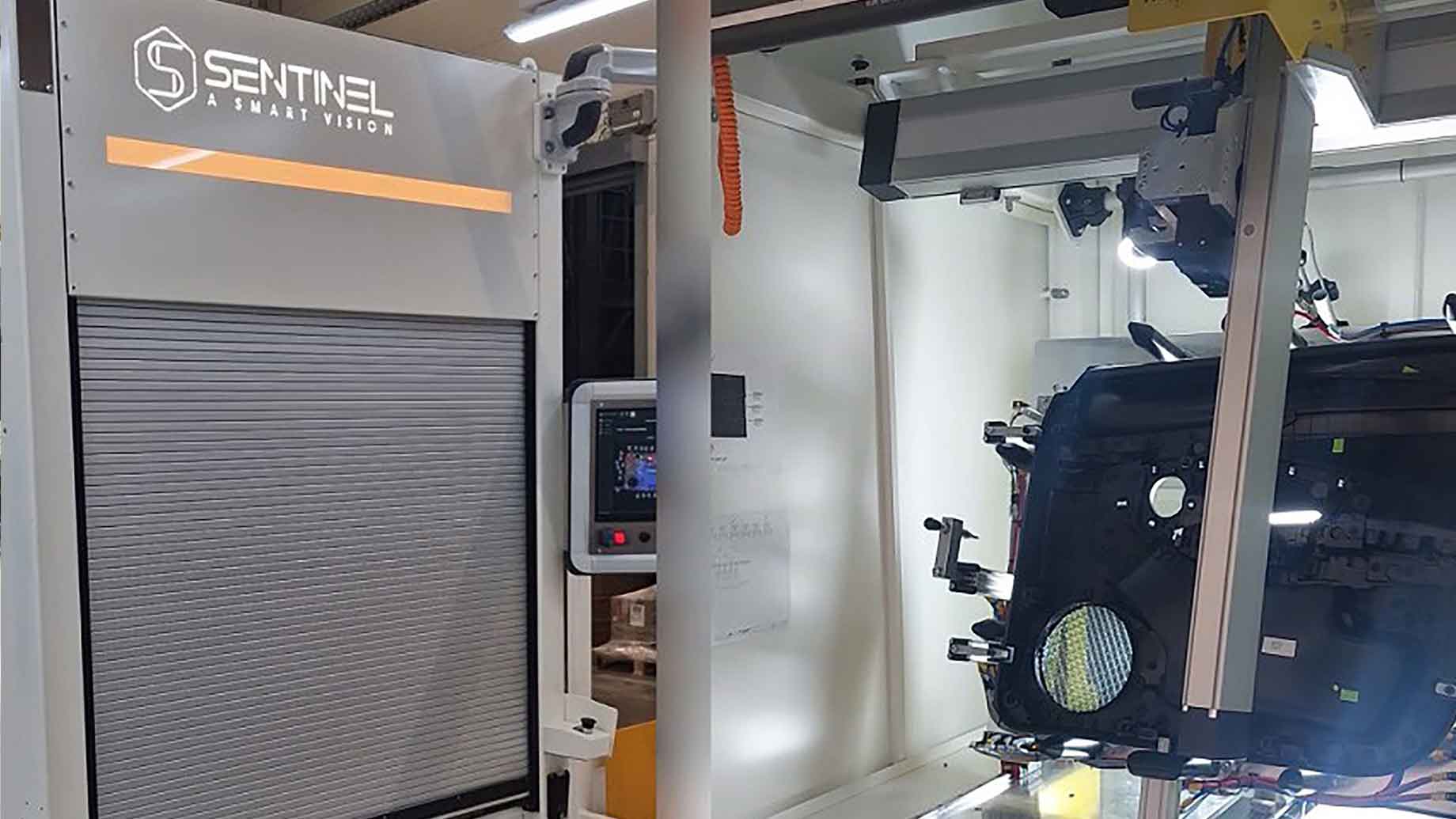
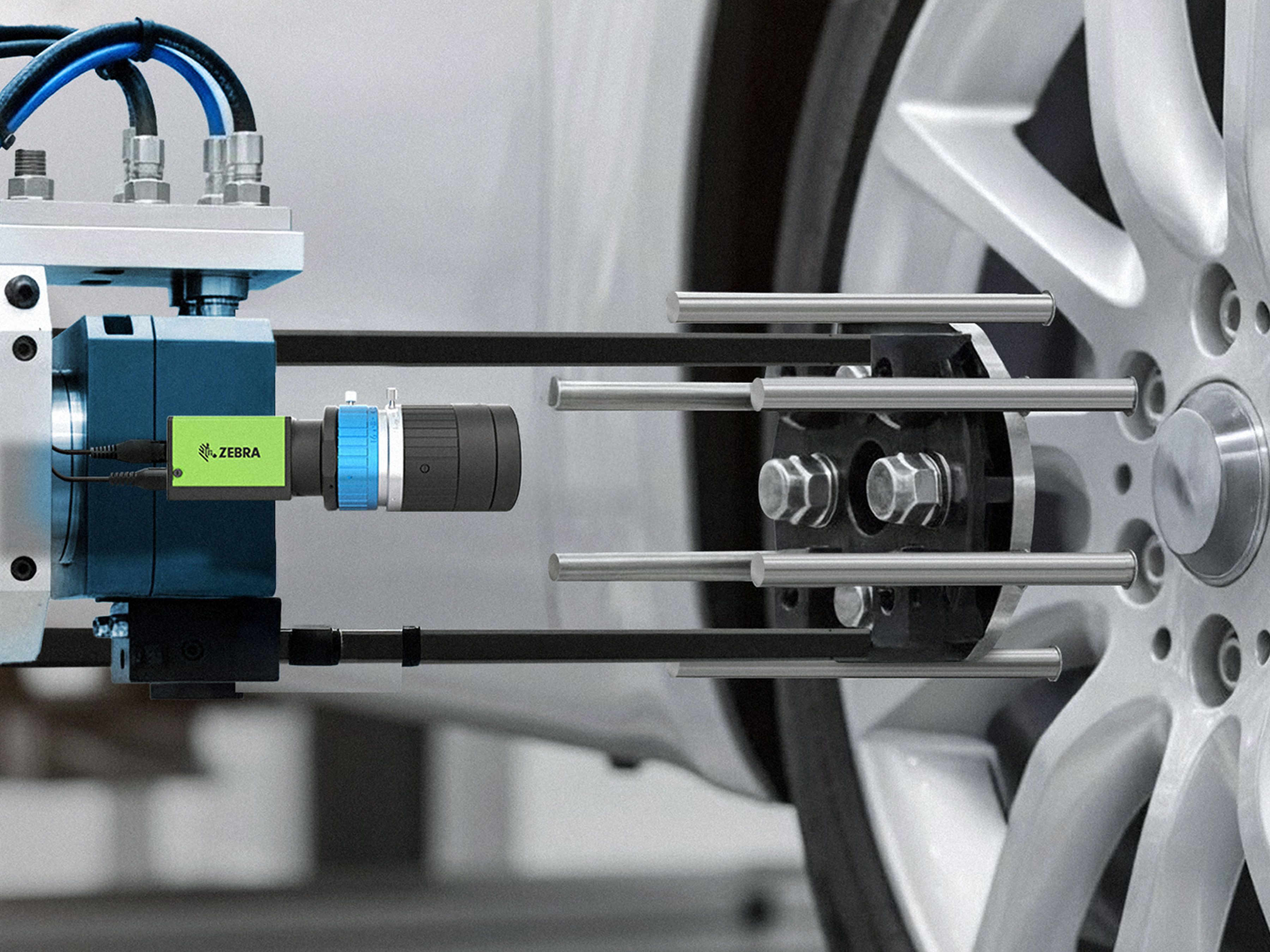
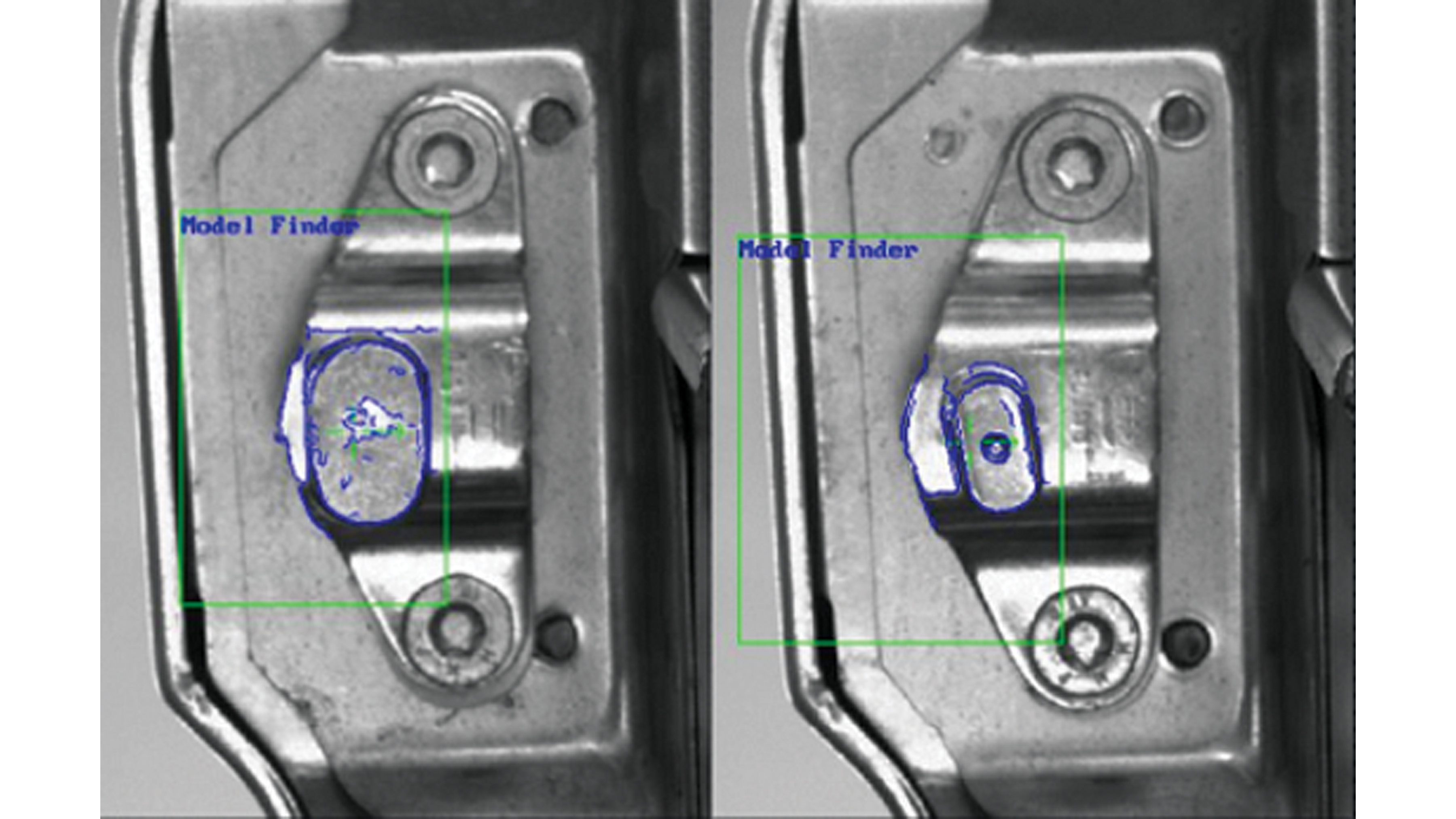
For inspecting automotive frame and body panel welding, the Zebra Iris GTX, a high-resolution smart camera, excels at rule-based inspections for clearly defined defects like weld nut inspections, missing components, or tooling alignment. Meanwhile, the Zebra NS42 smart vision sensor, optimized for deep learning based algorithms, handles more complex tasks like detecting subtle, irregular flaws (e.g., porosity, micro-cracks) and conducting visual surface inspections by learning from defect-free images. A combined approach allows manufacturers to implement a tiered inspection process: the Iris GTX performs rapid initial checks for common, well-defined errors, while the NS42 uses deep learning to identify more nuanced or unpredictable anomalies.
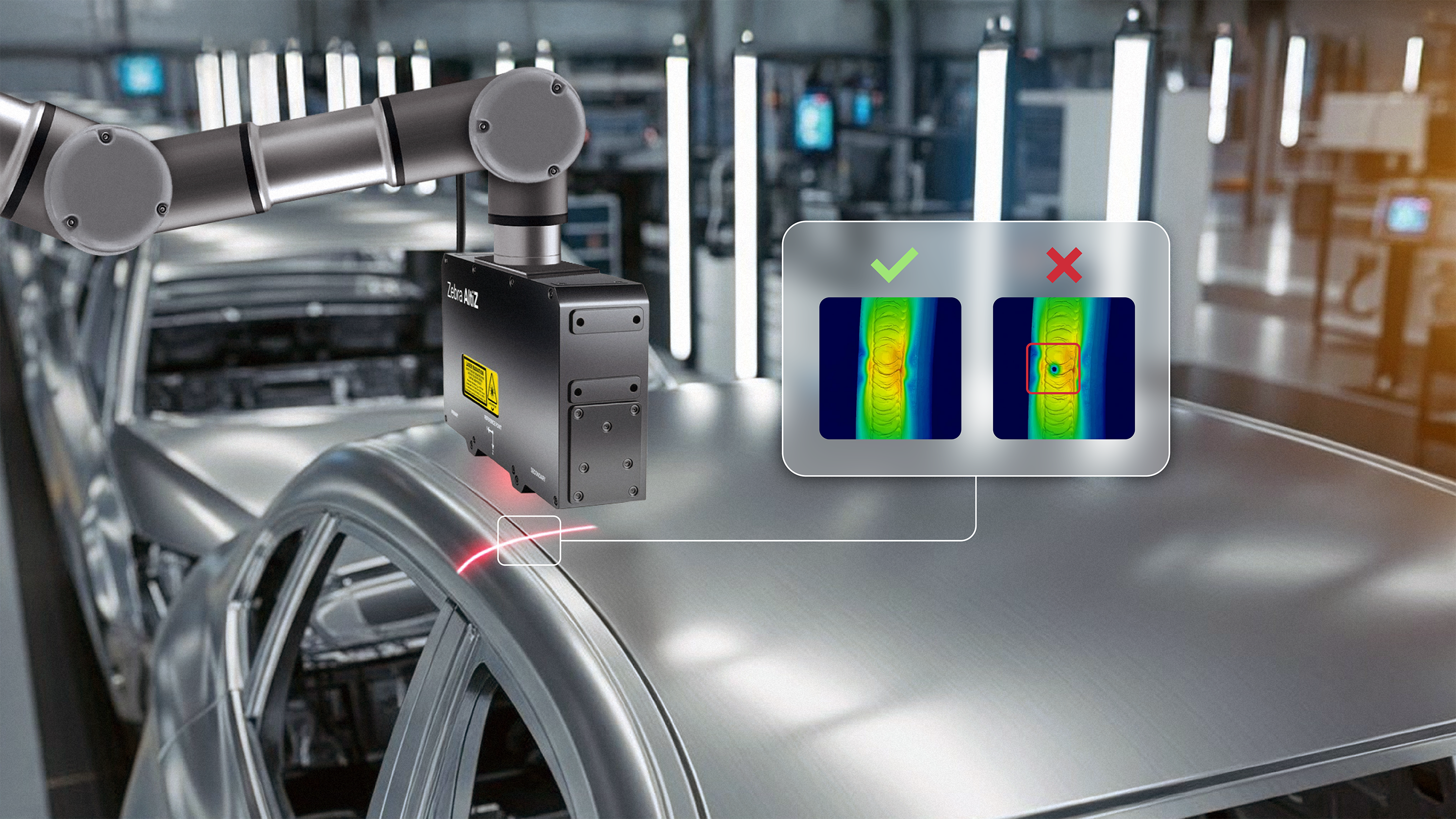
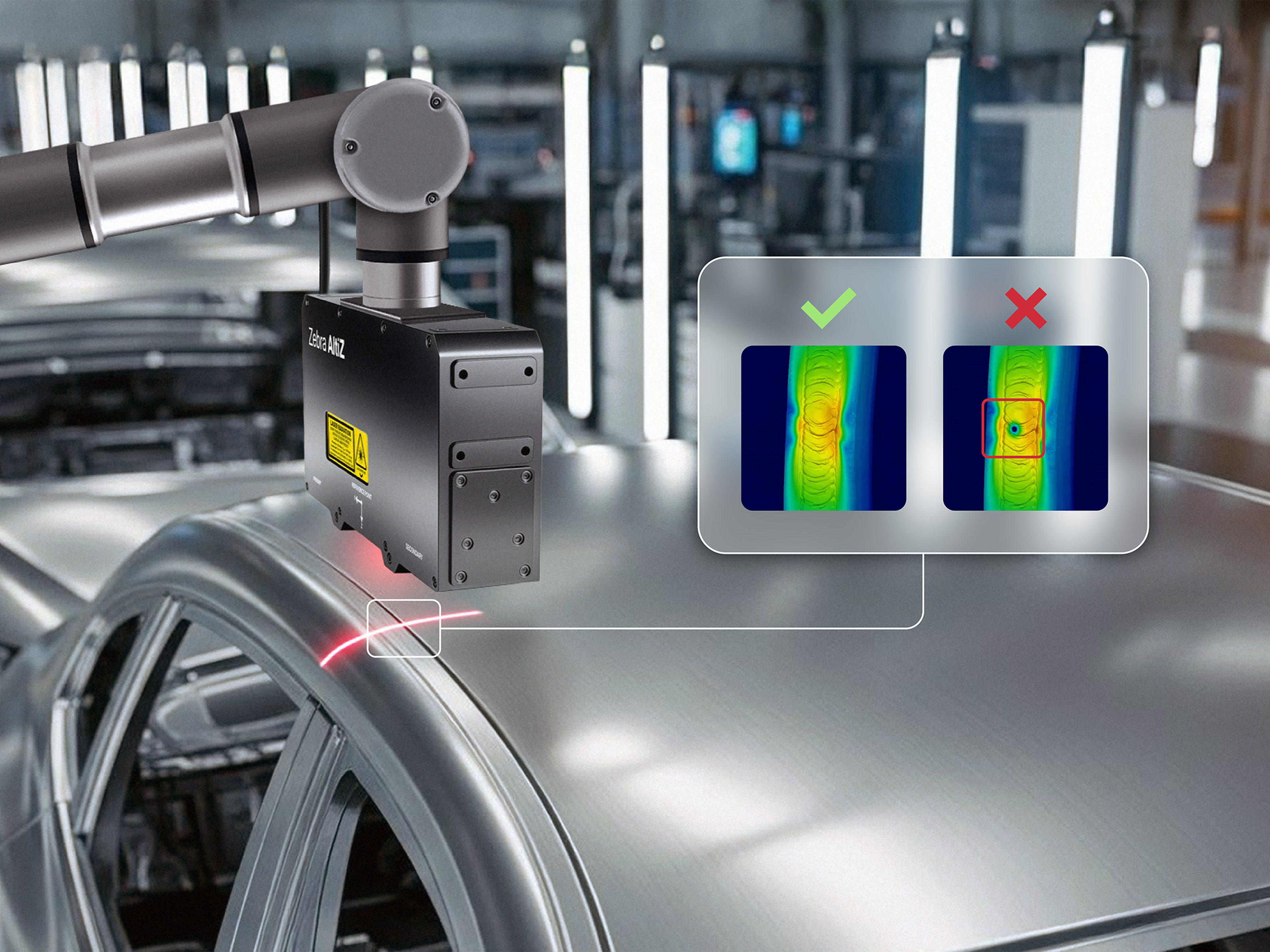
Add robot‑mounted 3D profiling for accuracy
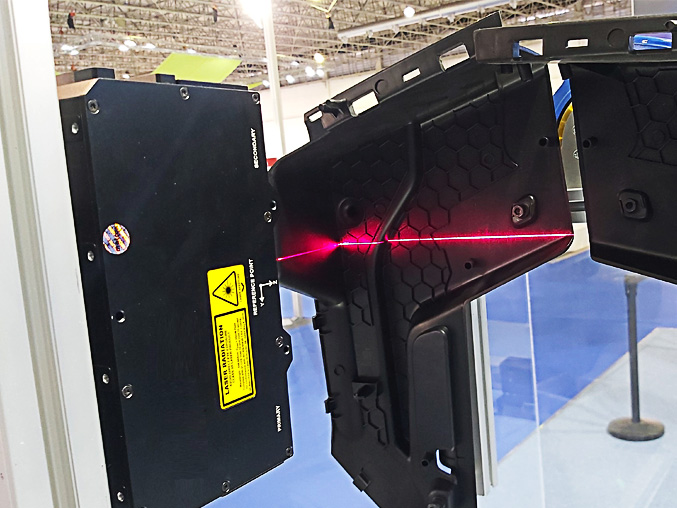
Zebra AltiZ profile sensors add precise 3D profiling for dense weld patterns. Robot‑mounted AltiZ profile sensors scan along weld seams to capture height and width profiles, then compute cross‑sections that confirm adequate size, gaps, and continuity—even on reflective aluminum or steel. The sensors synchronize with robot motion to maintain coverage around complex geometries to provide 100% inspection, boosting first‑pass yield at the production rate.
Integrate results and scale quality data
After verification of weld nuts, seams and studs, Aurora Design Assistant software reports labeled images, measurements, and pass/fail results to a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) or Quality Management System (QMS) for traceability, compliance, and root cause analysis. Plants trace each frame by VIN or serial ID, compare weld metrics over time, and trigger alerts when quality drifts. Standardized, version‑controlled inspection programs let teams roll out updates or consistent quality across lines.
Related Use Cases
Fixed Industrial Scanning and Machine Vision Success Stories
Talk to a Partner
Need more information on what solution is right for your needs? A partner can help.
Talk to Sales
Connect with our pre-sales team to get more information about our products, solutions and how to purchase.